지난 게시글에서는 집을 만들어 보았었는데요.
https://itadventure.tistory.com/687
바빌론JS - 땅위에 집 만들기 ( 자바스크립트로 )
오늘은 공식 튜토리얼의 집 짓기(영문)편을 크레이가 소화한 내용을 재구성한 집 만들기편을 진행하겠습니다.비주얼 스튜디오 코드로 진행할텐데요. 지난 게시글의 아래 코드를 참조해 주세요.
itadventure.tistory.com
벽면을 보면 뭔가 이상한게 있습니다.
벽돌의 방향이 한쪽 면은 가로 방향으로 맞게 보이는데,
다른 면은 방향이 세로인걸 볼 수 있는데요.

이 문제를 해결하려면 faceUV를 사용해야 합니다.
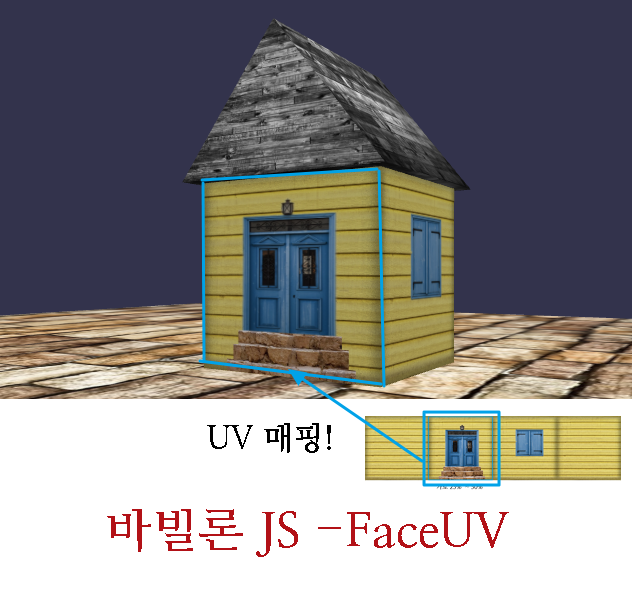

우선 아래와 같이 코드를 변경하는 것만으로 위 문제는 해결됩니다.
const faceUV = [];
var box = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateBox("house", {size: 1, faceUV: faceUV, wrap: true}, scene);faceUV 란 정육면체의 각 면마다 그림을 적용할 범위를 지정하는 방식인데요.
그 순서가 뒤(0), 앞(1), 좌(2), 우(3), 위(4), 아래(5)입니다.
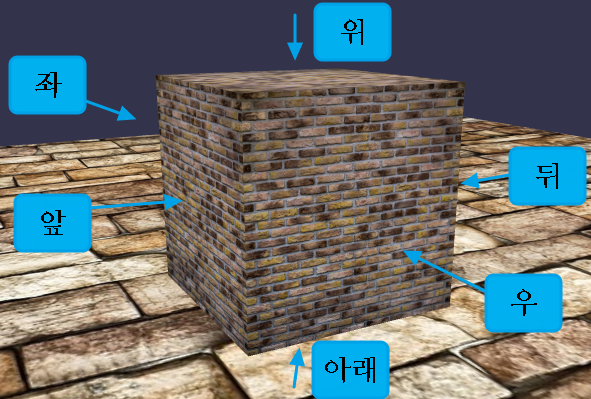
FaceUV를 이용하면 각 면마다 다른 이미지 영역을 적용할 수 있는데요.
이미지 영역을 적용한다니 말로 이해가 모호할 수 있어 한 면을 예시로 들어보겠습니다.
만일 뒷면(0)을 다른 면과 달리 이미지의 가로, 세로 절반 크기만 사용한다고 칩시다.

이 경우 50%를 0.5로 해서 아래 코드를 적용하면 되는데요.
결과는 아래와 같습니다. 면의 벽돌 밀도가 뭐가 달라도 다르지요?

이 방법을 응용하면, 아래 이미지 1장으로 상자집의 4면을 꾸밀 수 있습니다.
위, 아래면은 가려서 보이지 않으니 신경 안써도 되구요.
아래 이미지를 다운받아 wall-4.png 로 이름 변경 후 main.js 파일이 있는 곳에 저장해 주세요.
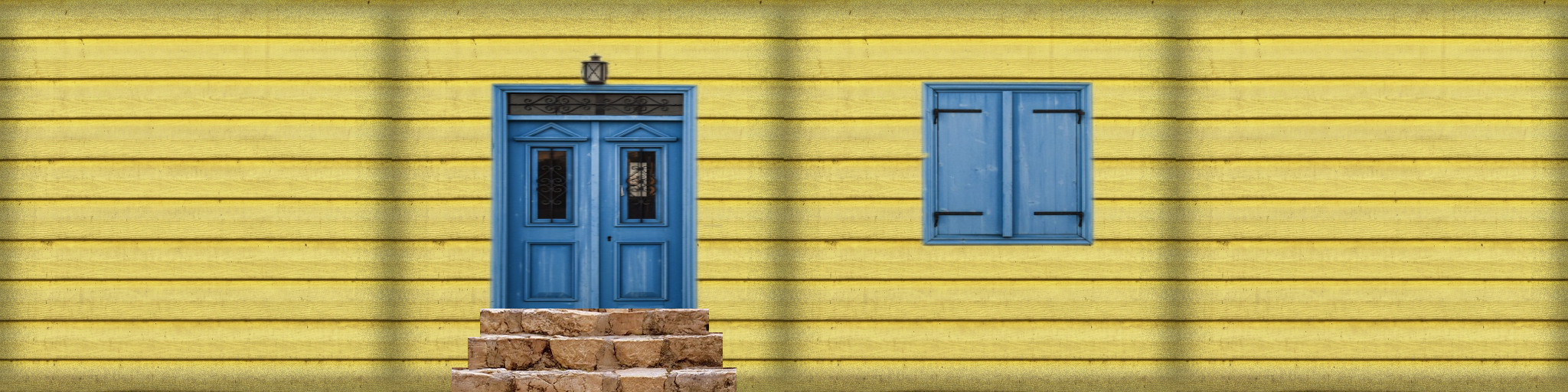

이미지 중 문이 들어가는 부분은 가로 영역의 범위는 25%~50%,
세로 영역은 처음부터 끝까지이니 0%~100%인데요.

이렇게 텍스쳐 영역을 비율로 정하는 것을 UV 좌표라고 합니다.
25% 는 0.25, 50%는 0.5로 표현하는데요.
UV좌표는 아래와 같이 정의할 수 있습니다.
(0.25, 0, 0.5, 1.0)4개의 면을 FaceUV 로 정의하는 코드는 아래와 같은데요.
const faceUV = [];
faceUV[0] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0.5, 0.0, 0.75, 1.0);
faceUV[1] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0.0, 0.0, 0.25, 1.0);
faceUV[2] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0.25, 0, 0.5, 1.0);
faceUV[3] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0.75, 0, 1.0, 1.0);FaceUV 코드 정의 영역을 위 코드로 변경하고,
wallMat 정의하는 코드도 아래와 같이 변경하면,
이미지의 각 영역이 나뉘어 집의 각 면에 배치되는 것을 보실 수 있습니다.
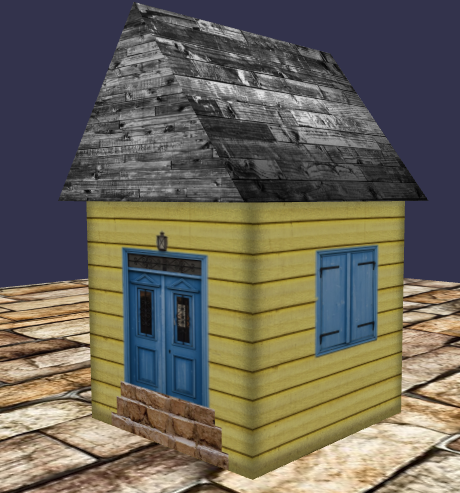

코드 정리 - 함수화
위 코드를 관리하기 쉽게 하려면 바닥, 상자, 지붕을 각각 함수화하는 것이 좋습니다.
함수화시킨 한번 기억해 놓으면 나중에 긴 코드 내용을 일일히 살펴보지 않아도 되기 때문이지요.바닥을 생성하는 아래 코드를
var ground = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateGround("crayground", {width: 10, height: 10}, scene);
const groundMat = new BABYLON.StandardMaterial("groundMat"); // 매트리얼 생성 ( 3D 에서는 모든 것이 메트리얼 )
groundMat.diffuseTexture = new BABYLON.Texture("./brick.jpg"); // 매트리얼에 그림을 적용
ground.material = groundMat; // 땅의 매트리얼에 적용아래와 같이 바꾸고
const ground = buildGround();아래 코드를 찾은 다음
return scene;
};그 아래에 함수를 넣어주면 됩니다. 이 때 scene 항목은 지워주셔야 에러가 안 납니다.
const buildGround = () => {
const ground = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateGround("crayground", {width: 10, height: 10});
const groundMat = new BABYLON.StandardMaterial("groundMat"); // 매트리얼 생성 ( 3D 에서는 모든 것이 메트리얼 )
groundMat.diffuseTexture = new BABYLON.Texture("./brick.jpg"); // 매트리얼에 그림을 적용
ground.material = groundMat; // 땅의 매트리얼에 적용
return ground;
}box와 roof 도 마찬가지 작업을 해주면 되는데요.
좀 복잡할 수 있으니 main.js 전체 파일 공개로 끝을 보려 합니다 :)
const canvas = document.getElementById("renderCanvas");
const engine = new BABYLON.Engine(canvas,true);
var createScene = function () {
// This creates a basic Babylon Scene object (non-mesh)
var scene = new BABYLON.Scene(engine);
// This creates and positions a free camera (non-mesh)
// var camera = new BABYLON.FreeCamera("camera1", new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 5, -10), scene);
var camera = new BABYLON.ArcRotateCamera("camera", BABYLON.Tools.ToRadians(90), BABYLON.Tools.ToRadians(65), 10, BABYLON.Vector3.Zero(), scene);
camera.wheelDeltaPercentage = 0.01;
// This targets the camera to scene origin
camera.setTarget(BABYLON.Vector3.Zero());
// This attaches the camera to the canvas
camera.attachControl(canvas, true);
// This creates a light, aiming 0,1,0 - to the sky (non-mesh)
var light = new BABYLON.HemisphericLight("light", new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 1, 0), scene);
// Default intensity is 1. Let's dim the light a small amount
light.intensity = 1.5;
const ground = buildGround(); // 바닥
const box = buildBox(); // 상자
const roof = buildRoof(); // 지붕
return scene;
};
// 바닥 함수화
const buildGround = () => {
const ground = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateGround("crayground", {width: 10, height: 10});
const groundMat = new BABYLON.StandardMaterial("groundMat"); // 매트리얼 생성 ( 3D 에서는 모든 것이 메트리얼 )
groundMat.diffuseTexture = new BABYLON.Texture("./brick.jpg"); // 매트리얼에 그림을 적용
ground.material = groundMat; // 땅의 매트리얼에 적용
return ground;
}
// 상자 함수화
const buildBox = () => {
const faceUV = [];
faceUV[0] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0.5, 0.0, 0.75, 1.0);
faceUV[1] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0.0, 0.0, 0.25, 1.0);
faceUV[2] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0.25, 0, 0.5, 1.0);
faceUV[3] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0.75, 0, 1.0, 1.0);
var box = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateBox("house", {size: 1, faceUV: faceUV, wrap: true});
box.position.y = 0.5;
// 박스 벽 매트리얼
const wallMat = new BABYLON.StandardMaterial("wallMat");
// wallMat.diffuseTexture = new BABYLON.Texture("./wall.jpg");
wallMat.diffuseTexture = new BABYLON.Texture("./wall-4.png");
box.material = wallMat;
return box;
}
// 지중 함수화
const buildRoof = () => {
const roof = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateCylinder("roof", {diameter: 1.3, height: 1.2, tessellation: 3});
roof.scaling.x = 0.75;
roof.rotation.z = Math.PI / 2;
roof.position.y = 1.22;
// 지붕 매트리얼
const roofMat = new BABYLON.StandardMaterial("rootMat");
roofMat.diffuseTexture = new BABYLON.Texture("./roof.jpg");
roof.material = roofMat;
return roof;
}
const scene = createScene();
engine.runRenderLoop(function () {
scene.render();
}
);
window.addEventListener("resize", function () {
engine.resize();
}
);
var camera = new BABYLON.ArcRotateCamera("camera", BABYLON.Tools.ToRadians(90), BABYLON.Tools.ToRadians(65), 10, BABYLON.Vector3.Zero(), scene);이제 함수화시켜 놓은 부분은 필요할 때만 살펴보면 됩니다.
아래 코드 3줄만 보고 또 이어서 뒤에 기능을 추가하면 되는데
추가한 기능은 또 다시 함수화하며 단순화하는 식으로 수시로 코드를 정리하는 습관을 들이는 것이
관리 측면에서 좋습니다.
전문 용어로는 코드 팩토링(Code Factoring)이라고도 하지요 :)
const ground = buildGround(); // 바닥
const box = buildBox(); // 상자
const roof = buildRoof(); // 지붕마무~리
바빌론JS 의 FaceUV에 대해 알아보았는데요.
도움이 되셨나 모르겠습니다 :)
오늘도 방문해주신 분들께 감사드립니다~!
다음 게시글 : https://itadventure.tistory.com/689
바빌론JS - 마을 꾸미기
지난 게시글에는 집을 만들고 표면을 꾸며보았지요.https://itadventure.tistory.com/688 바빌론 JS - 집의 벽 표면 지대로.지난 게시글에서는 집을 만들어 보았었는데요.https://itadventure.tistory.com/687 바빌
itadventure.tistory.com
